Blue lab-created diamonds are optically, chemically and physically identical to blue earth mined diamonds and are offered free of conflict and about 10% of the cost. They are typically offered in sizes smaller than 1.50 carats and come in a color range of Fancy Light Blue to Fancy Intense Blue.

Blue man-made diamonds.

Blue man-made diamonds color intensity.
Both mined and lab-created blue diamonds get their color from boron. While diamonds are made up of carbon, impurities within the stone exist. It is the introduction of these impurities, in this case boron, that will ultimately give the diamond its blue color. As a diamond grows, controlled amounts of boron are introduced into the growth cell which then become trapped in the diamond's lattice structure. Controlling the amount of boron in the growth cell allows the finished color to also be controlled. Once light enters the diamond, the boron will reflect back blue light.
Swipe left to see more.
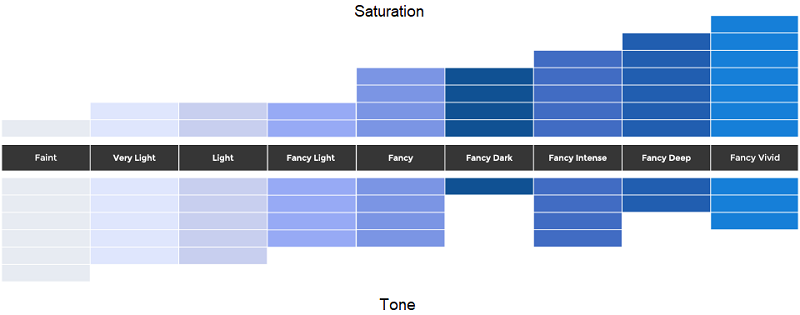
Blue man-made diamonds color levels.
It takes seven to ten days for one cycle in the growth machine to produce enough rough for a finished blue diamond up to 1.00 carat in size. The boron introduced during the growing process that gives a blue diamond its color actually helps the diamond grow quicker than a white diamond. Nonetheless, it will still grow slower than a yellow diamond.
Mined blue diamonds are incredibly rare in nature and can sell for anywhere between $200,000 to $500,000 per carat. A lab-created blue diamond costs about 10% of what a mined diamond costs. Most blue lab-created diamonds range from $7,000 to $12,000 per carat. Blue lab-created diamonds in fancy blue colors are the most expensive out of all the fancy colored diamonds due to the time and care needed to achieve the most desirable colors.
The majority of blue diamond roughs grow in a hexa-cubic shape. Round and cut corner shapes like, radiant, asscher, cushion and emerald are typically used to yield the most from the rough. Due to the hexa-cubic nature of the blue rough, princess cuts and elongated shapes like oval, marquise and pear are not typically produced.